|
MOAB
4.9.3pre
|
|
MOAB
4.9.3pre
|
LU decomposition of a matrix with complete pivoting, and related features. More...
#include <FullPivLU.h>
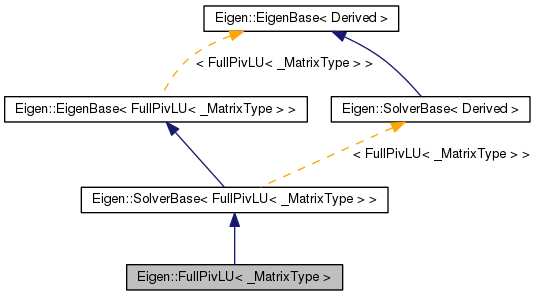

Public Types | |
| enum | { MaxRowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxColsAtCompileTime } |
| typedef _MatrixType | MatrixType |
| typedef SolverBase< FullPivLU > | Base |
| typedef internal::plain_row_type < MatrixType, StorageIndex > ::type | IntRowVectorType |
| typedef internal::plain_col_type < MatrixType, StorageIndex > ::type | IntColVectorType |
| typedef PermutationMatrix < ColsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime > | PermutationQType |
| typedef PermutationMatrix < RowsAtCompileTime, MaxRowsAtCompileTime > | PermutationPType |
| typedef MatrixType::PlainObject | PlainObject |
Public Member Functions | |
| FullPivLU () | |
| Default Constructor. | |
| FullPivLU (Index rows, Index cols) | |
| Default Constructor with memory preallocation. | |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| FullPivLU (const EigenBase< InputType > &matrix) | |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| FullPivLU & | compute (const EigenBase< InputType > &matrix) |
| const MatrixType & | matrixLU () const |
| Index | nonzeroPivots () const |
| RealScalar | maxPivot () const |
| const PermutationPType & | permutationP () const |
| const PermutationQType & | permutationQ () const |
| const internal::kernel_retval < FullPivLU > | kernel () const |
| const internal::image_retval < FullPivLU > | image (const MatrixType &originalMatrix) const |
| template<typename Rhs > | |
| const Solve< FullPivLU, Rhs > | solve (const MatrixBase< Rhs > &b) const |
| internal::traits< MatrixType > ::Scalar | determinant () const |
| FullPivLU & | setThreshold (const RealScalar &threshold) |
| FullPivLU & | setThreshold (Default_t) |
| RealScalar | threshold () const |
| Index | rank () const |
| Index | dimensionOfKernel () const |
| bool | isInjective () const |
| bool | isSurjective () const |
| bool | isInvertible () const |
| const Inverse< FullPivLU > | inverse () const |
| MatrixType | reconstructedMatrix () const |
| Index | rows () const |
| Index | cols () const |
| template<typename RhsType , typename DstType > | |
| EIGEN_DEVICE_FUNC void | _solve_impl (const RhsType &rhs, DstType &dst) const |
| template<bool Conjugate, typename RhsType , typename DstType > | |
| EIGEN_DEVICE_FUNC void | _solve_impl_transposed (const RhsType &rhs, DstType &dst) const |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | computeInPlace () |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | check_template_parameters () |
Protected Attributes | |
| MatrixType | m_lu |
| PermutationPType | m_p |
| PermutationQType | m_q |
| IntColVectorType | m_rowsTranspositions |
| IntRowVectorType | m_colsTranspositions |
| Index | m_det_pq |
| Index | m_nonzero_pivots |
| RealScalar | m_maxpivot |
| RealScalar | m_prescribedThreshold |
| bool | m_isInitialized |
| bool | m_usePrescribedThreshold |
LU decomposition of a matrix with complete pivoting, and related features.
| _MatrixType | the type of the matrix of which we are computing the LU decomposition |
This class represents a LU decomposition of any matrix, with complete pivoting: the matrix A is decomposed as 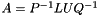 where L is unit-lower-triangular, U is upper-triangular, and P and Q are permutation matrices. This is a rank-revealing LU decomposition. The eigenvalues (diagonal coefficients) of U are sorted in such a way that any zeros are at the end.
where L is unit-lower-triangular, U is upper-triangular, and P and Q are permutation matrices. This is a rank-revealing LU decomposition. The eigenvalues (diagonal coefficients) of U are sorted in such a way that any zeros are at the end.
This decomposition provides the generic approach to solving systems of linear equations, computing the rank, invertibility, inverse, kernel, and determinant.
This LU decomposition is very stable and well tested with large matrices. However there are use cases where the SVD decomposition is inherently more stable and/or flexible. For example, when computing the kernel of a matrix, working with the SVD allows to select the smallest singular values of the matrix, something that the LU decomposition doesn't see.
The data of the LU decomposition can be directly accessed through the methods matrixLU(), permutationP(), permutationQ().
As an exemple, here is how the original matrix can be retrieved:
Output:
Definition at line 57 of file FullPivLU.h.
| typedef SolverBase<FullPivLU> Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::Base |
Reimplemented from Eigen::SolverBase< FullPivLU< _MatrixType > >.
Definition at line 62 of file FullPivLU.h.
| typedef internal::plain_col_type<MatrixType, StorageIndex>::type Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::IntColVectorType |
Definition at line 71 of file FullPivLU.h.
| typedef internal::plain_row_type<MatrixType, StorageIndex>::type Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::IntRowVectorType |
Definition at line 70 of file FullPivLU.h.
| typedef _MatrixType Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::MatrixType |
Definition at line 61 of file FullPivLU.h.
| typedef PermutationMatrix<RowsAtCompileTime, MaxRowsAtCompileTime> Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::PermutationPType |
Definition at line 73 of file FullPivLU.h.
| typedef PermutationMatrix<ColsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime> Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::PermutationQType |
Definition at line 72 of file FullPivLU.h.
| typedef MatrixType::PlainObject Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::PlainObject |
Definition at line 74 of file FullPivLU.h.
| anonymous enum |
Definition at line 66 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
MaxRowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxRowsAtCompileTime,
MaxColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxColsAtCompileTime
};
| Eigen::FullPivLU< MatrixType >::FullPivLU | ( | ) |
Default Constructor.
The default constructor is useful in cases in which the user intends to perform decompositions via LU::compute(const MatrixType&).
Definition at line 418 of file FullPivLU.h.
: m_isInitialized(false), m_usePrescribedThreshold(false) { }
| Eigen::FullPivLU< MatrixType >::FullPivLU | ( | Index | rows, |
| Index | cols | ||
| ) |
Default Constructor with memory preallocation.
Like the default constructor but with preallocation of the internal data according to the specified problem size.
Definition at line 424 of file FullPivLU.h.
: m_lu(rows, cols), m_p(rows), m_q(cols), m_rowsTranspositions(rows), m_colsTranspositions(cols), m_isInitialized(false), m_usePrescribedThreshold(false) { }
| Eigen::FullPivLU< MatrixType >::FullPivLU | ( | const EigenBase< InputType > & | matrix | ) | [explicit] |
Constructor.
| matrix | the matrix of which to compute the LU decomposition. It is required to be nonzero. |
Definition at line 437 of file FullPivLU.h.
: m_lu(matrix.rows(), matrix.cols()), m_p(matrix.rows()), m_q(matrix.cols()), m_rowsTranspositions(matrix.rows()), m_colsTranspositions(matrix.cols()), m_isInitialized(false), m_usePrescribedThreshold(false) { compute(matrix.derived()); }
| void Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::_solve_impl | ( | const RhsType & | rhs, |
| DstType & | dst | ||
| ) | const |
Definition at line 715 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
/* The decomposition PAQ = LU can be rewritten as A = P^{-1} L U Q^{-1}.
* So we proceed as follows:
* Step 1: compute c = P * rhs.
* Step 2: replace c by the solution x to Lx = c. Exists because L is invertible.
* Step 3: replace c by the solution x to Ux = c. May or may not exist.
* Step 4: result = Q * c;
*/
const Index rows = this->rows(),
cols = this->cols(),
nonzero_pivots = this->rank();
eigen_assert(rhs.rows() == rows);
const Index smalldim = (std::min)(rows, cols);
if(nonzero_pivots == 0)
{
dst.setZero();
return;
}
typename RhsType::PlainObject c(rhs.rows(), rhs.cols());
// Step 1
c = permutationP() * rhs;
// Step 2
m_lu.topLeftCorner(smalldim,smalldim)
.template triangularView<UnitLower>()
.solveInPlace(c.topRows(smalldim));
if(rows>cols)
c.bottomRows(rows-cols) -= m_lu.bottomRows(rows-cols) * c.topRows(cols);
// Step 3
m_lu.topLeftCorner(nonzero_pivots, nonzero_pivots)
.template triangularView<Upper>()
.solveInPlace(c.topRows(nonzero_pivots));
// Step 4
for(Index i = 0; i < nonzero_pivots; ++i)
dst.row(permutationQ().indices().coeff(i)) = c.row(i);
for(Index i = nonzero_pivots; i < m_lu.cols(); ++i)
dst.row(permutationQ().indices().coeff(i)).setZero();
}
| void Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::_solve_impl_transposed | ( | const RhsType & | rhs, |
| DstType & | dst | ||
| ) | const |
Definition at line 763 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
/* The decomposition PAQ = LU can be rewritten as A = P^{-1} L U Q^{-1},
* and since permutations are real and unitary, we can write this
* as A^T = Q U^T L^T P,
* So we proceed as follows:
* Step 1: compute c = Q^T rhs.
* Step 2: replace c by the solution x to U^T x = c. May or may not exist.
* Step 3: replace c by the solution x to L^T x = c.
* Step 4: result = P^T c.
* If Conjugate is true, replace "^T" by "^*" above.
*/
const Index rows = this->rows(), cols = this->cols(),
nonzero_pivots = this->rank();
eigen_assert(rhs.rows() == cols);
const Index smalldim = (std::min)(rows, cols);
if(nonzero_pivots == 0)
{
dst.setZero();
return;
}
typename RhsType::PlainObject c(rhs.rows(), rhs.cols());
// Step 1
c = permutationQ().inverse() * rhs;
if (Conjugate) {
// Step 2
m_lu.topLeftCorner(nonzero_pivots, nonzero_pivots)
.template triangularView<Upper>()
.adjoint()
.solveInPlace(c.topRows(nonzero_pivots));
// Step 3
m_lu.topLeftCorner(smalldim, smalldim)
.template triangularView<UnitLower>()
.adjoint()
.solveInPlace(c.topRows(smalldim));
} else {
// Step 2
m_lu.topLeftCorner(nonzero_pivots, nonzero_pivots)
.template triangularView<Upper>()
.transpose()
.solveInPlace(c.topRows(nonzero_pivots));
// Step 3
m_lu.topLeftCorner(smalldim, smalldim)
.template triangularView<UnitLower>()
.transpose()
.solveInPlace(c.topRows(smalldim));
}
// Step 4
PermutationPType invp = permutationP().inverse().eval();
for(Index i = 0; i < smalldim; ++i)
dst.row(invp.indices().coeff(i)) = c.row(i);
for(Index i = smalldim; i < rows; ++i)
dst.row(invp.indices().coeff(i)).setZero();
}
| static void Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::check_template_parameters | ( | ) | [inline, static, protected] |
Definition at line 400 of file FullPivLU.h.
| Index Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::cols | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Reimplemented from Eigen::EigenBase< FullPivLU< _MatrixType > >.
Definition at line 386 of file FullPivLU.h.
{ return m_lu.cols(); }
| FullPivLU< MatrixType > & Eigen::FullPivLU< MatrixType >::compute | ( | const EigenBase< InputType > & | matrix | ) |
Computes the LU decomposition of the given matrix.
| matrix | the matrix of which to compute the LU decomposition. It is required to be nonzero. |
Definition at line 451 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
check_template_parameters();
// the permutations are stored as int indices, so just to be sure:
eigen_assert(matrix.rows()<=NumTraits<int>::highest() && matrix.cols()<=NumTraits<int>::highest());
m_isInitialized = true;
m_lu = matrix.derived();
computeInPlace();
return *this;
}
| void Eigen::FullPivLU< MatrixType >::computeInPlace | ( | ) | [protected] |
Definition at line 467 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
const Index size = m_lu.diagonalSize();
const Index rows = m_lu.rows();
const Index cols = m_lu.cols();
// will store the transpositions, before we accumulate them at the end.
// can't accumulate on-the-fly because that will be done in reverse order for the rows.
m_rowsTranspositions.resize(m_lu.rows());
m_colsTranspositions.resize(m_lu.cols());
Index number_of_transpositions = 0; // number of NONTRIVIAL transpositions, i.e. m_rowsTranspositions[i]!=i
m_nonzero_pivots = size; // the generic case is that in which all pivots are nonzero (invertible case)
m_maxpivot = RealScalar(0);
for(Index k = 0; k < size; ++k)
{
// First, we need to find the pivot.
// biggest coefficient in the remaining bottom-right corner (starting at row k, col k)
Index row_of_biggest_in_corner, col_of_biggest_in_corner;
typedef internal::scalar_score_coeff_op<Scalar> Scoring;
typedef typename Scoring::result_type Score;
Score biggest_in_corner;
biggest_in_corner = m_lu.bottomRightCorner(rows-k, cols-k)
.unaryExpr(Scoring())
.maxCoeff(&row_of_biggest_in_corner, &col_of_biggest_in_corner);
row_of_biggest_in_corner += k; // correct the values! since they were computed in the corner,
col_of_biggest_in_corner += k; // need to add k to them.
if(biggest_in_corner==Score(0))
{
// before exiting, make sure to initialize the still uninitialized transpositions
// in a sane state without destroying what we already have.
m_nonzero_pivots = k;
for(Index i = k; i < size; ++i)
{
m_rowsTranspositions.coeffRef(i) = i;
m_colsTranspositions.coeffRef(i) = i;
}
break;
}
RealScalar abs_pivot = internal::abs_knowing_score<Scalar>()(m_lu(row_of_biggest_in_corner, col_of_biggest_in_corner), biggest_in_corner);
if(abs_pivot > m_maxpivot) m_maxpivot = abs_pivot;
// Now that we've found the pivot, we need to apply the row/col swaps to
// bring it to the location (k,k).
m_rowsTranspositions.coeffRef(k) = row_of_biggest_in_corner;
m_colsTranspositions.coeffRef(k) = col_of_biggest_in_corner;
if(k != row_of_biggest_in_corner) {
m_lu.row(k).swap(m_lu.row(row_of_biggest_in_corner));
++number_of_transpositions;
}
if(k != col_of_biggest_in_corner) {
m_lu.col(k).swap(m_lu.col(col_of_biggest_in_corner));
++number_of_transpositions;
}
// Now that the pivot is at the right location, we update the remaining
// bottom-right corner by Gaussian elimination.
if(k<rows-1)
m_lu.col(k).tail(rows-k-1) /= m_lu.coeff(k,k);
if(k<size-1)
m_lu.block(k+1,k+1,rows-k-1,cols-k-1).noalias() -= m_lu.col(k).tail(rows-k-1) * m_lu.row(k).tail(cols-k-1);
}
// the main loop is over, we still have to accumulate the transpositions to find the
// permutations P and Q
m_p.setIdentity(rows);
for(Index k = size-1; k >= 0; --k)
m_p.applyTranspositionOnTheRight(k, m_rowsTranspositions.coeff(k));
m_q.setIdentity(cols);
for(Index k = 0; k < size; ++k)
m_q.applyTranspositionOnTheRight(k, m_colsTranspositions.coeff(k));
m_det_pq = (number_of_transpositions%2) ? -1 : 1;
}
| internal::traits< MatrixType >::Scalar Eigen::FullPivLU< MatrixType >::determinant | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 551 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
eigen_assert(m_lu.rows() == m_lu.cols() && "You can't take the determinant of a non-square matrix!");
return Scalar(m_det_pq) * Scalar(m_lu.diagonal().prod());
}
| Index Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::dimensionOfKernel | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 325 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return cols() - rank();
}
| const internal::image_retval<FullPivLU> Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::image | ( | const MatrixType & | originalMatrix | ) | const [inline] |
| originalMatrix | the original matrix, of which *this is the LU decomposition. The reason why it is needed to pass it here, is that this allows a large optimization, as otherwise this method would need to reconstruct it from the LU decomposition. |
Example:
Output:
Definition at line 200 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return internal::image_retval<FullPivLU>(*this, originalMatrix);
}
| const Inverse<FullPivLU> Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::inverse | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 376 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
eigen_assert(m_lu.rows() == m_lu.cols() && "You can't take the inverse of a non-square matrix!");
return Inverse<FullPivLU>(*this);
}
| bool Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::isInjective | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 338 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return rank() == cols();
}
| bool Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::isInvertible | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 363 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return isInjective() && (m_lu.rows() == m_lu.cols());
}
| bool Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::isSurjective | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 351 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return rank() == rows();
}
| const internal::kernel_retval<FullPivLU> Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::kernel | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Example:
Output:
Definition at line 174 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return internal::kernel_retval<FullPivLU>(*this);
}
| const MatrixType& Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::matrixLU | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 116 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return m_lu;
}
| RealScalar Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::maxPivot | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 138 of file FullPivLU.h.
{ return m_maxpivot; }
| Index Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::nonzeroPivots | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 129 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return m_nonzero_pivots;
}
| const PermutationPType& Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::permutationP | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 144 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return m_p;
}
| const PermutationQType& Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::permutationQ | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 154 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return m_q;
}
| Index Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::rank | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 308 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
using std::abs;
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
RealScalar premultiplied_threshold = abs(m_maxpivot) * threshold();
Index result = 0;
for(Index i = 0; i < m_nonzero_pivots; ++i)
result += (abs(m_lu.coeff(i,i)) > premultiplied_threshold);
return result;
}
| MatrixType Eigen::FullPivLU< MatrixType >::reconstructedMatrix | ( | ) | const |
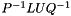 . This function is provided for debug purposes.
. This function is provided for debug purposes. Definition at line 562 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
const Index smalldim = (std::min)(m_lu.rows(), m_lu.cols());
// LU
MatrixType res(m_lu.rows(),m_lu.cols());
// FIXME the .toDenseMatrix() should not be needed...
res = m_lu.leftCols(smalldim)
.template triangularView<UnitLower>().toDenseMatrix()
* m_lu.topRows(smalldim)
.template triangularView<Upper>().toDenseMatrix();
// P^{-1}(LU)
res = m_p.inverse() * res;
// (P^{-1}LU)Q^{-1}
res = res * m_q.inverse();
return res;
}
| Index Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::rows | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Reimplemented from Eigen::EigenBase< FullPivLU< _MatrixType > >.
Definition at line 385 of file FullPivLU.h.
{ return m_lu.rows(); }
| FullPivLU& Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::setThreshold | ( | const RealScalar & | threshold | ) | [inline] |
Allows to prescribe a threshold to be used by certain methods, such as rank(), who need to determine when pivots are to be considered nonzero. This is not used for the LU decomposition itself.
When it needs to get the threshold value, Eigen calls threshold(). By default, this uses a formula to automatically determine a reasonable threshold. Once you have called the present method setThreshold(const RealScalar&), your value is used instead.
| threshold | The new value to use as the threshold. |
A pivot will be considered nonzero if its absolute value is strictly greater than 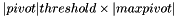 where maxpivot is the biggest pivot.
where maxpivot is the biggest pivot.
If you want to come back to the default behavior, call setThreshold(Default_t)
Definition at line 268 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
m_usePrescribedThreshold = true;
m_prescribedThreshold = threshold;
return *this;
}
| FullPivLU& Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::setThreshold | ( | Default_t | ) | [inline] |
Allows to come back to the default behavior, letting Eigen use its default formula for determining the threshold.
You should pass the special object Eigen::Default as parameter here.
lu.setThreshold(Eigen::Default);
See the documentation of setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
Definition at line 283 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
m_usePrescribedThreshold = false;
return *this;
}
| const Solve<FullPivLU, Rhs> Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::solve | ( | const MatrixBase< Rhs > & | b | ) | const [inline] |
| b | the right-hand-side of the equation to solve. Can be a vector or a matrix, the only requirement in order for the equation to make sense is that b.rows()==A.rows(), where A is the matrix of which *this is the LU decomposition. |
Example:
Output:
Reimplemented from Eigen::SolverBase< FullPivLU< _MatrixType > >.
Definition at line 228 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "LU is not initialized.");
return Solve<FullPivLU, Rhs>(*this, b.derived());
}
| RealScalar Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::threshold | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the threshold that will be used by certain methods such as rank().
See the documentation of setThreshold(const RealScalar&).
Definition at line 293 of file FullPivLU.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized || m_usePrescribedThreshold);
return m_usePrescribedThreshold ? m_prescribedThreshold
// this formula comes from experimenting (see "LU precision tuning" thread on the list)
// and turns out to be identical to Higham's formula used already in LDLt.
: NumTraits<Scalar>::epsilon() * m_lu.diagonalSize();
}
IntRowVectorType Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_colsTranspositions [protected] |
Definition at line 411 of file FullPivLU.h.
Index Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_det_pq [protected] |
Definition at line 412 of file FullPivLU.h.
bool Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_isInitialized [protected] |
Definition at line 414 of file FullPivLU.h.
MatrixType Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_lu [protected] |
Definition at line 407 of file FullPivLU.h.
RealScalar Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_maxpivot [protected] |
Definition at line 413 of file FullPivLU.h.
Index Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_nonzero_pivots [protected] |
Definition at line 412 of file FullPivLU.h.
PermutationPType Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_p [protected] |
Definition at line 408 of file FullPivLU.h.
RealScalar Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_prescribedThreshold [protected] |
Definition at line 413 of file FullPivLU.h.
PermutationQType Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_q [protected] |
Definition at line 409 of file FullPivLU.h.
IntColVectorType Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_rowsTranspositions [protected] |
Definition at line 410 of file FullPivLU.h.
bool Eigen::FullPivLU< _MatrixType >::m_usePrescribedThreshold [protected] |
Definition at line 414 of file FullPivLU.h.