|
MOAB
4.9.3pre
|
|
MOAB
4.9.3pre
|
Computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of general matrices. More...
#include <EigenSolver.h>

Public Types | |
| enum | { RowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::RowsAtCompileTime, ColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::ColsAtCompileTime, Options = MatrixType::Options, MaxRowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxColsAtCompileTime } |
| typedef _MatrixType | MatrixType |
Synonym for the template parameter _MatrixType. | |
| typedef MatrixType::Scalar | Scalar |
| Scalar type for matrices of type MatrixType. | |
| typedef NumTraits< Scalar >::Real | RealScalar |
| typedef Eigen::Index | Index |
| typedef std::complex< RealScalar > | ComplexScalar |
| Complex scalar type for MatrixType. | |
| typedef Matrix< ComplexScalar, ColsAtCompileTime, 1, Options &~RowMajor, MaxColsAtCompileTime, 1 > | EigenvalueType |
| Type for vector of eigenvalues as returned by eigenvalues(). | |
| typedef Matrix< ComplexScalar, RowsAtCompileTime, ColsAtCompileTime, Options, MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime > | EigenvectorsType |
| Type for matrix of eigenvectors as returned by eigenvectors(). | |
Public Member Functions | |
| EigenSolver () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| EigenSolver (Index size) | |
| Default constructor with memory preallocation. | |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| EigenSolver (const EigenBase< InputType > &matrix, bool computeEigenvectors=true) | |
| Constructor; computes eigendecomposition of given matrix. | |
| EigenvectorsType | eigenvectors () const |
| Returns the eigenvectors of given matrix. | |
| const MatrixType & | pseudoEigenvectors () const |
| Returns the pseudo-eigenvectors of given matrix. | |
| MatrixType | pseudoEigenvalueMatrix () const |
| Returns the block-diagonal matrix in the pseudo-eigendecomposition. | |
| const EigenvalueType & | eigenvalues () const |
| Returns the eigenvalues of given matrix. | |
| template<typename InputType > | |
| EigenSolver & | compute (const EigenBase< InputType > &matrix, bool computeEigenvectors=true) |
| Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix. | |
| ComputationInfo | info () const |
| EigenSolver & | setMaxIterations (Index maxIters) |
| Sets the maximum number of iterations allowed. | |
| Index | getMaxIterations () |
| Returns the maximum number of iterations. | |
Protected Types | |
| typedef Matrix< Scalar, ColsAtCompileTime, 1, Options &~RowMajor, MaxColsAtCompileTime, 1 > | ColumnVectorType |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | check_template_parameters () |
Protected Attributes | |
| MatrixType | m_eivec |
| EigenvalueType | m_eivalues |
| bool | m_isInitialized |
| bool | m_eigenvectorsOk |
| ComputationInfo | m_info |
| RealSchur< MatrixType > | m_realSchur |
| MatrixType | m_matT |
| ColumnVectorType | m_tmp |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | doComputeEigenvectors () |
Computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors of general matrices.
| _MatrixType | the type of the matrix of which we are computing the eigendecomposition; this is expected to be an instantiation of the Matrix class template. Currently, only real matrices are supported. |
The eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix  are scalars
are scalars 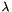 and vectors
and vectors 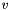 such that
such that 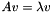 . If
. If 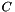 is a diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues on the diagonal, and
is a diagonal matrix with the eigenvalues on the diagonal, and 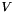 is a matrix with the eigenvectors as its columns, then
is a matrix with the eigenvectors as its columns, then 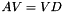 . The matrix
. The matrix 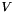 is almost always invertible, in which case we have
is almost always invertible, in which case we have 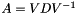 . This is called the eigendecomposition.
. This is called the eigendecomposition.
The eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix may be complex, even when the matrix is real. However, we can choose real matrices 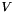 and
and 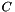 satisfying
satisfying 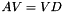 , just like the eigendecomposition, if the matrix
, just like the eigendecomposition, if the matrix 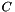 is not required to be diagonal, but if it is allowed to have blocks of the form
is not required to be diagonal, but if it is allowed to have blocks of the form
![\[ \begin{bmatrix} u & v \\ -v & u \end{bmatrix} \]](form_53.png)
(where 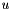 and
and 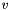 are real numbers) on the diagonal. These blocks correspond to complex eigenvalue pairs
are real numbers) on the diagonal. These blocks correspond to complex eigenvalue pairs 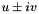 . We call this variant of the eigendecomposition the pseudo-eigendecomposition.
. We call this variant of the eigendecomposition the pseudo-eigendecomposition.
Call the function compute() to compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a given matrix. Alternatively, you can use the EigenSolver(const MatrixType&, bool) constructor which computes the eigenvalues and eigenvectors at construction time. Once the eigenvalue and eigenvectors are computed, they can be retrieved with the eigenvalues() and eigenvectors() functions. The pseudoEigenvalueMatrix() and pseudoEigenvectors() methods allow the construction of the pseudo-eigendecomposition.
The documentation for EigenSolver(const MatrixType&, bool) contains an example of the typical use of this class.
Definition at line 64 of file EigenSolver.h.
typedef Matrix<Scalar, ColsAtCompileTime, 1, Options & ~RowMajor, MaxColsAtCompileTime, 1> Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::ColumnVectorType [protected] |
Definition at line 319 of file EigenSolver.h.
| typedef std::complex<RealScalar> Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::ComplexScalar |
Complex scalar type for MatrixType.
This is std::complex<Scalar> if Scalar is real (e.g., float or double) and just Scalar if Scalar is complex.
Definition at line 90 of file EigenSolver.h.
| typedef Matrix<ComplexScalar, ColsAtCompileTime, 1, Options & ~RowMajor, MaxColsAtCompileTime, 1> Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::EigenvalueType |
Type for vector of eigenvalues as returned by eigenvalues().
This is a column vector with entries of type ComplexScalar. The length of the vector is the size of MatrixType.
Definition at line 97 of file EigenSolver.h.
| typedef Matrix<ComplexScalar, RowsAtCompileTime, ColsAtCompileTime, Options, MaxRowsAtCompileTime, MaxColsAtCompileTime> Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::EigenvectorsType |
Type for matrix of eigenvectors as returned by eigenvectors().
This is a square matrix with entries of type ComplexScalar. The size is the same as the size of MatrixType.
Definition at line 104 of file EigenSolver.h.
| typedef Eigen::Index Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::Index |
Definition at line 82 of file EigenSolver.h.
| typedef _MatrixType Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::MatrixType |
Synonym for the template parameter _MatrixType.
Definition at line 69 of file EigenSolver.h.
| typedef NumTraits<Scalar>::Real Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::RealScalar |
Definition at line 81 of file EigenSolver.h.
| typedef MatrixType::Scalar Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::Scalar |
Scalar type for matrices of type MatrixType.
Definition at line 80 of file EigenSolver.h.
| anonymous enum |
Definition at line 71 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
RowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::RowsAtCompileTime,
ColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::ColsAtCompileTime,
Options = MatrixType::Options,
MaxRowsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxRowsAtCompileTime,
MaxColsAtCompileTime = MatrixType::MaxColsAtCompileTime
};
| Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::EigenSolver | ( | ) | [inline] |
Default constructor.
The default constructor is useful in cases in which the user intends to perform decompositions via EigenSolver::compute(const MatrixType&, bool).
Definition at line 113 of file EigenSolver.h.
: m_eivec(), m_eivalues(), m_isInitialized(false), m_realSchur(), m_matT(), m_tmp() {}
| Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::EigenSolver | ( | Index | size | ) | [inline, explicit] |
Default constructor with memory preallocation.
Like the default constructor but with preallocation of the internal data according to the specified problem size.
Definition at line 121 of file EigenSolver.h.
: m_eivec(size, size), m_eivalues(size), m_isInitialized(false), m_eigenvectorsOk(false), m_realSchur(size), m_matT(size, size), m_tmp(size) {}
| Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::EigenSolver | ( | const EigenBase< InputType > & | matrix, |
| bool | computeEigenvectors = true |
||
| ) | [inline, explicit] |
Constructor; computes eigendecomposition of given matrix.
| [in] | matrix | Square matrix whose eigendecomposition is to be computed. |
| [in] | computeEigenvectors | If true, both the eigenvectors and the eigenvalues are computed; if false, only the eigenvalues are computed. |
This constructor calls compute() to compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
Example:
Output:
Definition at line 147 of file EigenSolver.h.
: m_eivec(matrix.rows(), matrix.cols()), m_eivalues(matrix.cols()), m_isInitialized(false), m_eigenvectorsOk(false), m_realSchur(matrix.cols()), m_matT(matrix.rows(), matrix.cols()), m_tmp(matrix.cols()) { compute(matrix.derived(), computeEigenvectors); }
| static void Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::check_template_parameters | ( | ) | [inline, static, protected] |
Definition at line 305 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
EIGEN_STATIC_ASSERT_NON_INTEGER(Scalar);
EIGEN_STATIC_ASSERT(!NumTraits<Scalar>::IsComplex, NUMERIC_TYPE_MUST_BE_REAL);
}
| EigenSolver< MatrixType > & Eigen::EigenSolver< MatrixType >::compute | ( | const EigenBase< InputType > & | matrix, |
| bool | computeEigenvectors = true |
||
| ) |
Computes eigendecomposition of given matrix.
| [in] | matrix | Square matrix whose eigendecomposition is to be computed. |
| [in] | computeEigenvectors | If true, both the eigenvectors and the eigenvalues are computed; if false, only the eigenvalues are computed. |
*this This function computes the eigenvalues of the real matrix matrix. The eigenvalues() function can be used to retrieve them. If computeEigenvectors is true, then the eigenvectors are also computed and can be retrieved by calling eigenvectors().
The matrix is first reduced to real Schur form using the RealSchur class. The Schur decomposition is then used to compute the eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
The cost of the computation is dominated by the cost of the Schur decomposition, which is very approximately 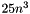 (where
(where 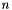 is the size of the matrix) if
is the size of the matrix) if computeEigenvectors is true, and 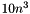 if
if computeEigenvectors is false.
This method reuses of the allocated data in the EigenSolver object.
Example:
Output:
Definition at line 377 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
check_template_parameters();
using std::sqrt;
using std::abs;
using numext::isfinite;
eigen_assert(matrix.cols() == matrix.rows());
// Reduce to real Schur form.
m_realSchur.compute(matrix.derived(), computeEigenvectors);
m_info = m_realSchur.info();
if (m_info == Success)
{
m_matT = m_realSchur.matrixT();
if (computeEigenvectors)
m_eivec = m_realSchur.matrixU();
// Compute eigenvalues from matT
m_eivalues.resize(matrix.cols());
Index i = 0;
while (i < matrix.cols())
{
if (i == matrix.cols() - 1 || m_matT.coeff(i+1, i) == Scalar(0))
{
m_eivalues.coeffRef(i) = m_matT.coeff(i, i);
if(!(isfinite)(m_eivalues.coeffRef(i)))
{
m_isInitialized = true;
m_eigenvectorsOk = false;
m_info = NumericalIssue;
return *this;
}
++i;
}
else
{
Scalar p = Scalar(0.5) * (m_matT.coeff(i, i) - m_matT.coeff(i+1, i+1));
Scalar z;
// Compute z = sqrt(abs(p * p + m_matT.coeff(i+1, i) * m_matT.coeff(i, i+1)));
// without overflow
{
Scalar t0 = m_matT.coeff(i+1, i);
Scalar t1 = m_matT.coeff(i, i+1);
Scalar maxval = numext::maxi<Scalar>(abs(p),numext::maxi<Scalar>(abs(t0),abs(t1)));
t0 /= maxval;
t1 /= maxval;
Scalar p0 = p/maxval;
z = maxval * sqrt(abs(p0 * p0 + t0 * t1));
}
m_eivalues.coeffRef(i) = ComplexScalar(m_matT.coeff(i+1, i+1) + p, z);
m_eivalues.coeffRef(i+1) = ComplexScalar(m_matT.coeff(i+1, i+1) + p, -z);
if(!((isfinite)(m_eivalues.coeffRef(i)) && (isfinite)(m_eivalues.coeffRef(i+1))))
{
m_isInitialized = true;
m_eigenvectorsOk = false;
m_info = NumericalIssue;
return *this;
}
i += 2;
}
}
// Compute eigenvectors.
if (computeEigenvectors)
doComputeEigenvectors();
}
m_isInitialized = true;
m_eigenvectorsOk = computeEigenvectors;
return *this;
}
| void Eigen::EigenSolver< MatrixType >::doComputeEigenvectors | ( | ) | [private] |
Definition at line 476 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
using std::abs;
const Index size = m_eivec.cols();
const Scalar eps = NumTraits<Scalar>::epsilon();
// inefficient! this is already computed in RealSchur
Scalar norm(0);
for (Index j = 0; j < size; ++j)
{
norm += m_matT.row(j).segment((std::max)(j-1,Index(0)), size-(std::max)(j-1,Index(0))).cwiseAbs().sum();
}
// Backsubstitute to find vectors of upper triangular form
if (norm == Scalar(0))
{
return;
}
for (Index n = size-1; n >= 0; n--)
{
Scalar p = m_eivalues.coeff(n).real();
Scalar q = m_eivalues.coeff(n).imag();
// Scalar vector
if (q == Scalar(0))
{
Scalar lastr(0), lastw(0);
Index l = n;
m_matT.coeffRef(n,n) = 1.0;
for (Index i = n-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
Scalar w = m_matT.coeff(i,i) - p;
Scalar r = m_matT.row(i).segment(l,n-l+1).dot(m_matT.col(n).segment(l, n-l+1));
if (m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag() < Scalar(0))
{
lastw = w;
lastr = r;
}
else
{
l = i;
if (m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag() == Scalar(0))
{
if (w != Scalar(0))
m_matT.coeffRef(i,n) = -r / w;
else
m_matT.coeffRef(i,n) = -r / (eps * norm);
}
else // Solve real equations
{
Scalar x = m_matT.coeff(i,i+1);
Scalar y = m_matT.coeff(i+1,i);
Scalar denom = (m_eivalues.coeff(i).real() - p) * (m_eivalues.coeff(i).real() - p) + m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag() * m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag();
Scalar t = (x * lastr - lastw * r) / denom;
m_matT.coeffRef(i,n) = t;
if (abs(x) > abs(lastw))
m_matT.coeffRef(i+1,n) = (-r - w * t) / x;
else
m_matT.coeffRef(i+1,n) = (-lastr - y * t) / lastw;
}
// Overflow control
Scalar t = abs(m_matT.coeff(i,n));
if ((eps * t) * t > Scalar(1))
m_matT.col(n).tail(size-i) /= t;
}
}
}
else if (q < Scalar(0) && n > 0) // Complex vector
{
Scalar lastra(0), lastsa(0), lastw(0);
Index l = n-1;
// Last vector component imaginary so matrix is triangular
if (abs(m_matT.coeff(n,n-1)) > abs(m_matT.coeff(n-1,n)))
{
m_matT.coeffRef(n-1,n-1) = q / m_matT.coeff(n,n-1);
m_matT.coeffRef(n-1,n) = -(m_matT.coeff(n,n) - p) / m_matT.coeff(n,n-1);
}
else
{
std::complex<Scalar> cc = cdiv<Scalar>(Scalar(0),-m_matT.coeff(n-1,n),m_matT.coeff(n-1,n-1)-p,q);
m_matT.coeffRef(n-1,n-1) = numext::real(cc);
m_matT.coeffRef(n-1,n) = numext::imag(cc);
}
m_matT.coeffRef(n,n-1) = Scalar(0);
m_matT.coeffRef(n,n) = Scalar(1);
for (Index i = n-2; i >= 0; i--)
{
Scalar ra = m_matT.row(i).segment(l, n-l+1).dot(m_matT.col(n-1).segment(l, n-l+1));
Scalar sa = m_matT.row(i).segment(l, n-l+1).dot(m_matT.col(n).segment(l, n-l+1));
Scalar w = m_matT.coeff(i,i) - p;
if (m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag() < Scalar(0))
{
lastw = w;
lastra = ra;
lastsa = sa;
}
else
{
l = i;
if (m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag() == RealScalar(0))
{
std::complex<Scalar> cc = cdiv(-ra,-sa,w,q);
m_matT.coeffRef(i,n-1) = numext::real(cc);
m_matT.coeffRef(i,n) = numext::imag(cc);
}
else
{
// Solve complex equations
Scalar x = m_matT.coeff(i,i+1);
Scalar y = m_matT.coeff(i+1,i);
Scalar vr = (m_eivalues.coeff(i).real() - p) * (m_eivalues.coeff(i).real() - p) + m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag() * m_eivalues.coeff(i).imag() - q * q;
Scalar vi = (m_eivalues.coeff(i).real() - p) * Scalar(2) * q;
if ((vr == Scalar(0)) && (vi == Scalar(0)))
vr = eps * norm * (abs(w) + abs(q) + abs(x) + abs(y) + abs(lastw));
std::complex<Scalar> cc = cdiv(x*lastra-lastw*ra+q*sa,x*lastsa-lastw*sa-q*ra,vr,vi);
m_matT.coeffRef(i,n-1) = numext::real(cc);
m_matT.coeffRef(i,n) = numext::imag(cc);
if (abs(x) > (abs(lastw) + abs(q)))
{
m_matT.coeffRef(i+1,n-1) = (-ra - w * m_matT.coeff(i,n-1) + q * m_matT.coeff(i,n)) / x;
m_matT.coeffRef(i+1,n) = (-sa - w * m_matT.coeff(i,n) - q * m_matT.coeff(i,n-1)) / x;
}
else
{
cc = cdiv(-lastra-y*m_matT.coeff(i,n-1),-lastsa-y*m_matT.coeff(i,n),lastw,q);
m_matT.coeffRef(i+1,n-1) = numext::real(cc);
m_matT.coeffRef(i+1,n) = numext::imag(cc);
}
}
// Overflow control
Scalar t = numext::maxi<Scalar>(abs(m_matT.coeff(i,n-1)),abs(m_matT.coeff(i,n)));
if ((eps * t) * t > Scalar(1))
m_matT.block(i, n-1, size-i, 2) /= t;
}
}
// We handled a pair of complex conjugate eigenvalues, so need to skip them both
n--;
}
else
{
eigen_assert(0 && "Internal bug in EigenSolver (INF or NaN has not been detected)"); // this should not happen
}
}
// Back transformation to get eigenvectors of original matrix
for (Index j = size-1; j >= 0; j--)
{
m_tmp.noalias() = m_eivec.leftCols(j+1) * m_matT.col(j).segment(0, j+1);
m_eivec.col(j) = m_tmp;
}
}
| const EigenvalueType& Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::eigenvalues | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the eigenvalues of given matrix.
The eigenvalues are repeated according to their algebraic multiplicity, so there are as many eigenvalues as rows in the matrix. The eigenvalues are not sorted in any particular order.
Example:
Output:
Definition at line 244 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "EigenSolver is not initialized.");
return m_eivalues;
}
| EigenSolver< MatrixType >::EigenvectorsType Eigen::EigenSolver< MatrixType >::eigenvectors | ( | ) | const |
Returns the eigenvectors of given matrix.
computeEigenvectors was set to true (the default).Column 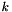 of the returned matrix is an eigenvector corresponding to eigenvalue number
of the returned matrix is an eigenvector corresponding to eigenvalue number 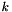 as returned by eigenvalues(). The eigenvectors are normalized to have (Euclidean) norm equal to one. The matrix returned by this function is the matrix
as returned by eigenvalues(). The eigenvectors are normalized to have (Euclidean) norm equal to one. The matrix returned by this function is the matrix 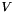 in the eigendecomposition
in the eigendecomposition 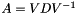 , if it exists.
, if it exists.
Example:
Output:
Definition at line 344 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "EigenSolver is not initialized.");
eigen_assert(m_eigenvectorsOk && "The eigenvectors have not been computed together with the eigenvalues.");
Index n = m_eivec.cols();
EigenvectorsType matV(n,n);
for (Index j=0; j<n; ++j)
{
if (internal::isMuchSmallerThan(numext::imag(m_eivalues.coeff(j)), numext::real(m_eivalues.coeff(j))) || j+1==n)
{
// we have a real eigen value
matV.col(j) = m_eivec.col(j).template cast<ComplexScalar>();
matV.col(j).normalize();
}
else
{
// we have a pair of complex eigen values
for (Index i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
matV.coeffRef(i,j) = ComplexScalar(m_eivec.coeff(i,j), m_eivec.coeff(i,j+1));
matV.coeffRef(i,j+1) = ComplexScalar(m_eivec.coeff(i,j), -m_eivec.coeff(i,j+1));
}
matV.col(j).normalize();
matV.col(j+1).normalize();
++j;
}
}
return matV;
}
| Index Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::getMaxIterations | ( | ) | [inline] |
Returns the maximum number of iterations.
Definition at line 295 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
return m_realSchur.getMaxIterations();
}
| ComputationInfo Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::info | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 281 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "EigenSolver is not initialized.");
return m_info;
}
| MatrixType Eigen::EigenSolver< MatrixType >::pseudoEigenvalueMatrix | ( | ) | const |
Returns the block-diagonal matrix in the pseudo-eigendecomposition.
The matrix 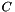 returned by this function is real and block-diagonal. The blocks on the diagonal are either 1-by-1 or 2-by-2 blocks of the form
returned by this function is real and block-diagonal. The blocks on the diagonal are either 1-by-1 or 2-by-2 blocks of the form 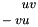 . These blocks are not sorted in any particular order. The matrix
. These blocks are not sorted in any particular order. The matrix 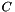 and the matrix
and the matrix 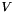 returned by pseudoEigenvectors() satisfy
returned by pseudoEigenvectors() satisfy 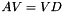 .
.
Definition at line 324 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "EigenSolver is not initialized.");
Index n = m_eivalues.rows();
MatrixType matD = MatrixType::Zero(n,n);
for (Index i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
if (internal::isMuchSmallerThan(numext::imag(m_eivalues.coeff(i)), numext::real(m_eivalues.coeff(i))))
matD.coeffRef(i,i) = numext::real(m_eivalues.coeff(i));
else
{
matD.template block<2,2>(i,i) << numext::real(m_eivalues.coeff(i)), numext::imag(m_eivalues.coeff(i)),
-numext::imag(m_eivalues.coeff(i)), numext::real(m_eivalues.coeff(i));
++i;
}
}
return matD;
}
| const MatrixType& Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::pseudoEigenvectors | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the pseudo-eigenvectors of given matrix.
computeEigenvectors was set to true (the default).The real matrix 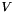 returned by this function and the block-diagonal matrix
returned by this function and the block-diagonal matrix 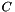 returned by pseudoEigenvalueMatrix() satisfy
returned by pseudoEigenvalueMatrix() satisfy 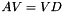 .
.
Example:
Output:
Definition at line 199 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
eigen_assert(m_isInitialized && "EigenSolver is not initialized.");
eigen_assert(m_eigenvectorsOk && "The eigenvectors have not been computed together with the eigenvalues.");
return m_eivec;
}
| EigenSolver& Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::setMaxIterations | ( | Index | maxIters | ) | [inline] |
Sets the maximum number of iterations allowed.
Definition at line 288 of file EigenSolver.h.
{
m_realSchur.setMaxIterations(maxIters);
return *this;
}
bool Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_eigenvectorsOk [protected] |
Definition at line 314 of file EigenSolver.h.
EigenvalueType Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_eivalues [protected] |
Definition at line 312 of file EigenSolver.h.
MatrixType Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_eivec [protected] |
Definition at line 311 of file EigenSolver.h.
ComputationInfo Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_info [protected] |
Definition at line 315 of file EigenSolver.h.
bool Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_isInitialized [protected] |
Definition at line 313 of file EigenSolver.h.
MatrixType Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_matT [protected] |
Definition at line 317 of file EigenSolver.h.
RealSchur<MatrixType> Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_realSchur [protected] |
Definition at line 316 of file EigenSolver.h.
ColumnVectorType Eigen::EigenSolver< _MatrixType >::m_tmp [protected] |
Definition at line 320 of file EigenSolver.h.